The Importance of Grain Drying in Modern Agriculture
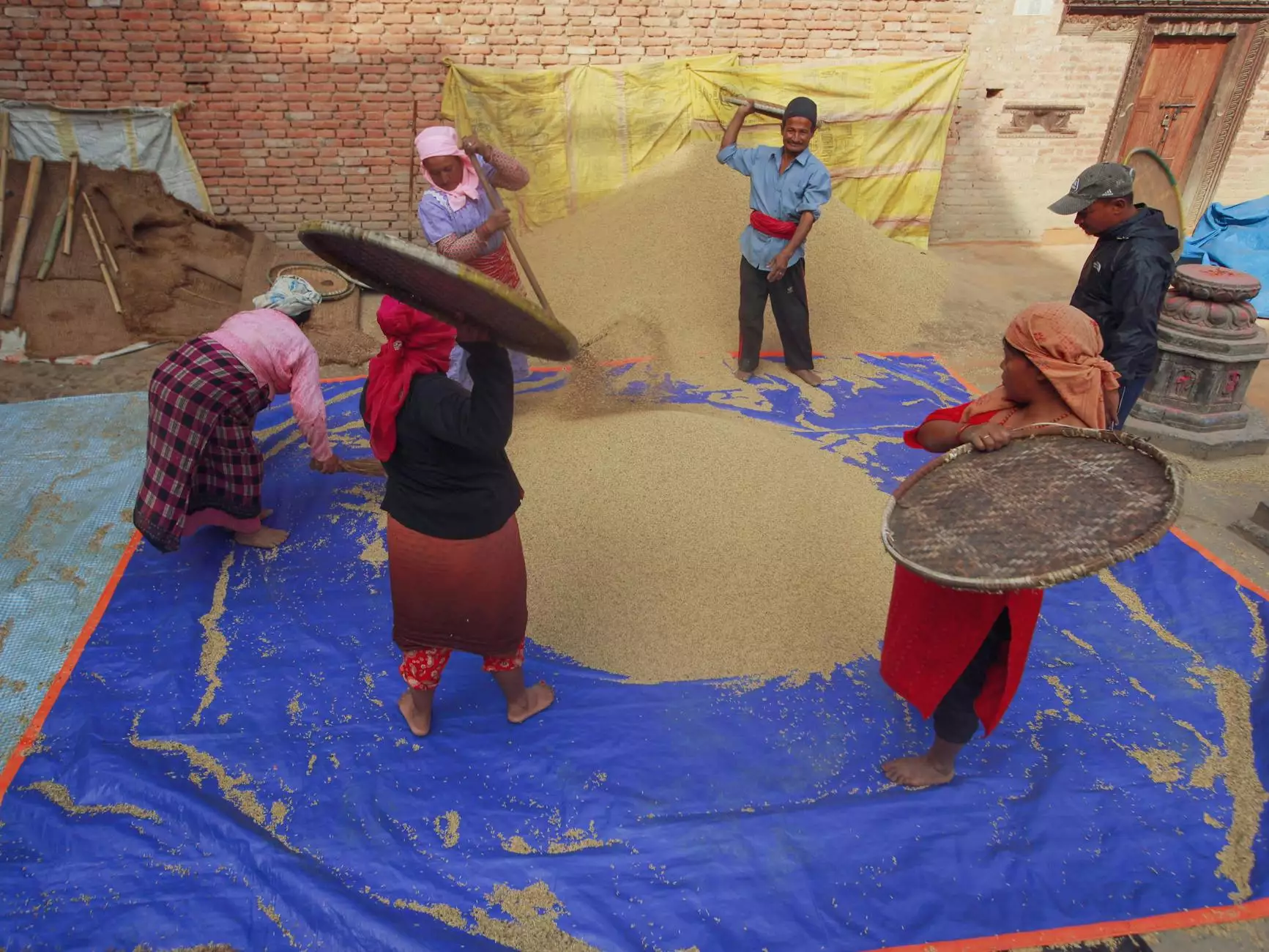

Understanding Grain Drying
Grain drying is a crucial process in agriculture that involves removing excess moisture from harvested crops. This practice is essential not only for preserving the quality of the grain but also for enhancing marketability. With the right drying techniques, farmers can significantly reduce the risk of spoilage, pest infestations, and mycotoxin production—factors that can drastically impact crop value.
Why is Grain Drying So Important?
The importance of grain drying cannot be overstated, as it directly influences agricultural productivity and profitability. Here are several reasons why this process is vital in modern farming:
- Preservation of Quality: Drying grain helps in maintaining its nutritional value and prevents quality degradation.
- Prevention of Spoilage: Moisture-rich environments are breeding grounds for mold and bacteria, which can lead to spoilage and waste.
- Enhancing Market Value: Dried grains typically command better prices in the market compared to moist ones.
- Improved Storage Life: Properly dried grains can be stored for longer periods without losing quality.
- Pest Control: Reduced moisture levels deter pests from invading and damaging stored grains.
The Grain Drying Process
The grain drying process can vary depending on the type of grain, moisture content, and environmental conditions. Below are the primary steps involved in efficient grain drying:
1. Harvesting
Grains should be harvested at the right moisture level to maximize drying efficiency. Ideal moisture content varies by grain type, but generally, it should be around 20-25% for effective drying.
2. Pre-Drying Preparation
This involves cleaning and grading the grain to remove impurities, stones, and damaged grains, which can affect the drying process and final product quality.
3. Drying Methods
Several methods can be employed for drying grains, including:
- Natural Air Drying: Utilizing ambient air conditions to dry grains by spreading them out in thin layers.
- Mechanical Drying: Using grain dryers that apply heat and airflow to remove moisture efficiently.
- Sun Drying: Harnessing solar energy in clear weather, although it is less reliable and slower compared to mechanical methods.
4. Cooling and Storing
Once the grains are dried to the optimal moisture level (usually around 13-14%), they should be cooled before storage to reduce condensation and maintain quality. Proper storage conditions are as important as the drying process itself.
Impact of Moisture Content on Grain Quality
The impact of moisture content on grain quality is profound. Grains with high moisture content can undergo various negative transformations:
- Increased Risk of Mold: Excess moisture creates a perfect environment for molds, which can release harmful mycotoxins.
- Loss of Nutritional Value: Moist grains are prone to nutrient degradation, leading to subpar quality.
- Difficulty in Processing: High moisture can make grains harder to process, affecting downstream products.
- Increased Energy Costs: Higher moisture levels require more energy for drying, increasing operational costs.
Economic Benefits of Proper Grain Drying
Implementing effective grain drying techniques is not just about maintaining quality; it also brings substantial economic benefits to farmers.
1. Enhanced Profitability
By ensuring that grains are fully dried, farmers can see an increase in profitability. Drier grains fetch higher market prices, which can significantly enhance revenue.
2. Reduction in Waste
Proper drying can minimize waste due to spoilage, thus improving the overall yield from the harvest.
3. Lower Storage Costs
Dried grains incur lower storage costs as they are less susceptible to pests and spoilage, reducing overall expenditure.
Technological Advances in Grain Drying
Recent advancements in grain drying technology have revolutionized the way farmers approach this vital step. Automated and energy-efficient drying systems are now more accessible.
1. Continuous Flow Dryers
Continuous flow dryers have enabled faster drying times and are designed to handle large volumes of grain efficiently.
2. Sensor Technology
Modern sensors can monitor moisture content in real-time, allowing farmers to adjust drying conditions for optimal results.
3. Mobile Drying Units
Portable drying units enable farmers to dry grain on-site, minimizing transport and enhancing efficiency during the harvest season.
Best Practices for Grain Drying
To maximize the benefits of grain drying, farmers should adhere to best practices that not only enhance efficiency but also ensure quality:
- Regular Maintenance of Drying Equipment: Keeping your drying equipment in top condition ensures maximum efficiency.
- Monitor Conditions: Always check temperature and humidity levels during the drying process.
- Utilize Insulation: Proper insulation in storage facilities can help maintain optimal conditions for stored grain.
- Educate Staff: Provide education and training for those involved in harvesting and drying processes to improve techniques.
The Future of Grain Drying
As the agriculture industry continues to evolve, the importance of grain drying will only become more pronounced. Sustainable practices and technological advancements will shape the future of this essential process. By adopting new methods and technologies, farmers can ensure that their operations are efficient, profitable, and environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the importance of grain drying is integral to successful farming practices. It impacts quality, storage, marketability, and overall profitability. Farmers who understand and implement effective drying techniques position themselves for better outcomes, ensuring they meet both their business goals and the demands of an evolving market.